Types Of Bowling Ball Cores – Asymmetrical Vs Symmetrical
The core of the bowling ball is the only thing that needs technical details to understand and also there is no visual way to examine the type of core nor can we open the bowling ball.
In bowling, what types of bowling ball cores are being used in any specific ball? or what characteristics of any specific core will help you a lot in choosing the right reaction type of bowling ball.
This guide is specifically designed to understand in-depth about what are the different types of cores used in a bowling ball and how they can affect your game experience.
Types Of Bowling Ball Cores
In the modern world of bowling, manufacturers design bowling balls in different shapes, weights, and sizes. Likewise, bowling ball cores are further classified into 3 categories, each with its own characteristics.
In the preliminary section, two terms, RG and differential, are used to describe the core you need to understand.
The radius of gyration also called RG measured in Inches is specified for the distance from the axis for rotation till that point where the body focuses without any difference or change in moment of inertia. More precisely, the RG can be calculated when the bowling ball revs up, and most commonly two types of RG are high and low where low RG rev up earlier as compared to high RG.
The second terminology is the differential that is connected with the value of low or high RG values and it specifies the overall hook whether it will be low, medium or high.
Pancake-type Core
The name of the core specifies its shape that formed in Pan-Cake or visualized in puddle shape. In the early era of bowling, pancakes were used widely in the construction of bowling balls.
Pancake is the most common and traditional design of core that is normally used in spare or straight reaction bowling balls. Also, it can be found on the entry-level urethane or reactive resin bowling balls.
Moreover, concerning the exact shape of the pancake core, the low performance-based pancake core is often the same, just there is low and high RG differential funda you can find TUH.
The bowling balls based on the pancake core typically feature high RG with low differential and deliver low hook potential.
Symmetrical Core
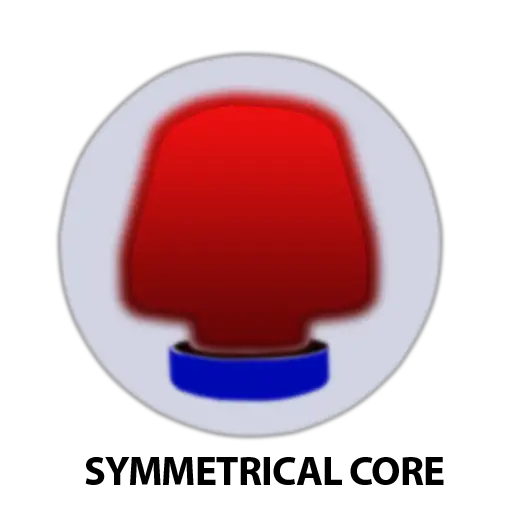

In modern bowling, the symmetrical core is used widely in advanced balls. In a symmetrical core, two-piece bowling balls with a large core are found, but there is no three mass of inertia compared to the Asymmetrical core.
The asymmetrical core is further split into two types: axisymmetric and non-axisymmetric. A popular example of axisymmetric is the light bulb core that we commonly hear in pro shops or bowling clubs or read in bowling balls manuals.
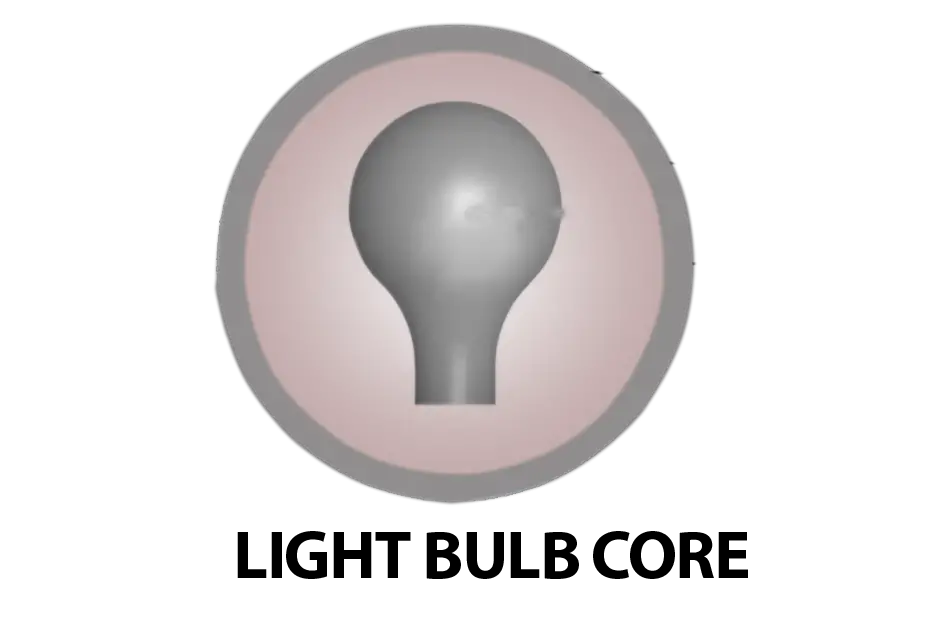

The main difference between axisymmetric and non-axisymmetric is that the axisymmetric forms in two dimensions around a mid axis whereas non-axisymmetric is more complex and can be multi-dimensional.
To specify whether the bowling ball is symmetrical or asymmetrical as it can’t be identified by seeing it. To recognize, if the bowling ball has a low intermediate differential (More Precisely, the low intermediate differential below 0.008 or 5%) or is not defined by the manufacturer then most likely it’s a symmetrical core.
A bowling ball equipped with symmetrical core rolls is smoother and more predictable while interacting with the fraction on the lane. Moreover, the hook is less comparatively and suitable for low rev players. The symmetrical core is more likely built for bowling balls with straight reactions.
Asymmetrical Core

Compared to a symmetrical core, asymmetrical cores have three masses of inertia while symmetrical cores have two. Bowling balls with asymmetrical cores come with a high intermediate differential and the range starts from 0.008 to 0.025 or above 5%.
Asymmetrical cores are suitable for those players who want bowling balls with more hooks. Additionally, it rolls on the lane accurate and confidently against the fraction and can be a good pick for players with high rev.
It comes in a variety of different shapes and sizes and can be used for variation of RG and differential. The strength of the core can be measured by its intermediate differential.
Asymmetrical Vs Symmetrical Bowling Ball
The main difference between asymmetrical vs symmetrical bowling balls is the intermediate differential of the core whereas the rest of the cores are declared as asymmetrical cores except below 0.008 intermediate differentials. Asymmetric gives aggressive motion with hook whereas symmetrical delivers smoother and straight.
Characteristics of Bowling Ball Cores
Pan-cake Core
Symmetrical Core
Asymmetrical Core
What’s the Difference Between Two-Piece & Three-Piece Bowling Ball Cores?
The main difference between two-piece and three-piece is that two-piece are constructed in such an arrangement where the coverstock is thick and wide with dynamic weight blocks in a specific shape whereas three pieces have narrow coverstock and pancake-shaped weight block with a large area of filler material
How Do I Choose A Bowling Ball Core
To choose a bowling ball core widely depends on what kind of reaction you want in bowling. As a matter of bowling motion, somehow it also depends on the cores just like the coverstocks of the bowling balls. If we talk about pancake cores, it comes with low intermediate difference which means they have the least hook potential and are most probably used for straight shots.
On the other side, a symmetrical core also comes with a little hook with a somehow low intermediate difference but comparatively has a smoother and predictable motion that is suitable for low-speed players. However, an asymmetrical core is designed with a high intermediate differential that carries high hook potential and is appropriate for fast-speed players.
Conclusion:
Whether you buy any bowling ball, if you don’t consider the types of bowling ball core, you’re about to make a big mistake.
In today’s era, there are several bowling ball manufacturers that build bowling balls for different players from beginners to advanced levels, and different kinds of reactions.
If you’re a beginner and want to learn bowling then a bowling ball with a pancake or symmetrical core would be best whereas if you throw a curve shot or hooking then asymmetrical but the reaction of bowling balls is also affected by other factors in different types of bowling balls.

William Martin is a passionate bowler who spends most of his weekends playing the sport. With years of intense experience under his belt, William decided to share his knowledge by creating BOWLING OCEAN. Join me on this journey to explore the world of bowling and discover the tips and tricks to becoming a pro.






